How Does Air Brake Work: Getting Insights From Physics & Engineering
Air brakes are a type of brake that uses compressed air to create enough pressure to stop or slow down the wheels. Air brakes are commonly found on trains and passenger cars.
There are two main types of air brakes: vacuum and air. Vacuum brakes operate on the negative pressure principle. Therefore, almost zero pressure is created in front of each wheel when the vacuum is created, which makes the pressure slow or stops the wheel’s rotation.
Air brakes use compressed air at high speed to generate enough force to slow or stop the rotation. The more pressure you apply to your brakes, the faster your vehicle’s motion will stop.
This braking system can be very complex because it consists of many parts. The most important part of an air brake is the vehicle’s air reservoir, which stores compressed air at high pressure.
When the driver needs to stop or slow down the vehicle, he pulls the brake lever. This movement activates a valve that releases some of the pressure in the reservoir into an airline that goes to each bus wheel. The driver can control the desired braking force by regulating the pressure from the reservoir.
How do air brakes work?
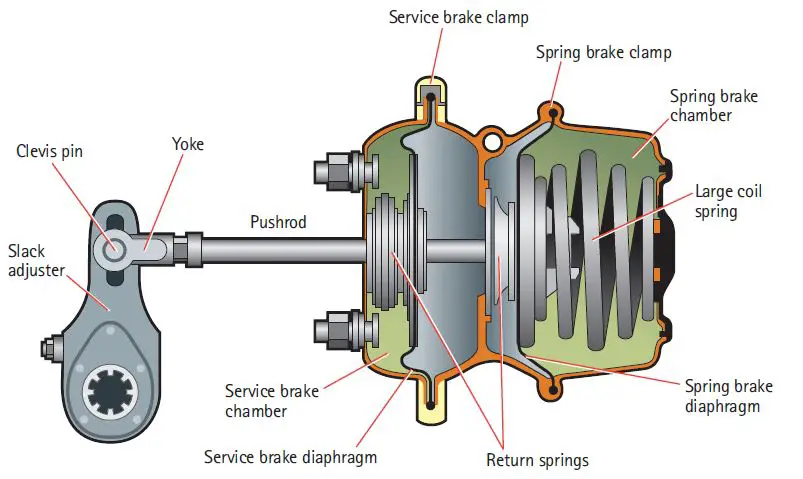
Brake lines, drums, brake shoes, brake pads, rods, stacks, brake pads, and brake pedals are all part of the air brake system.
The brake line connects the brake cylinders to the train line. It contains a mixture of air and water. As the train moves forward, the brake line forces the air out through the brake cylinders. This creates a vacuum in front of each brake shoe. The brake shoes then press against the brake drum. This creates friction, which slows down the rotation of the wheels and, thus, the train.
A brake cylinder is a device that contains compressed air. A brake cylinder is connected to the brake pipe. The brake cylinder is connected to the brake pad. The brake pad is located between the brake cylinder and the brake shoes. The brake pad is connected to the brake rod. The brake rod is connected to the brake linkage. Brake drums are connected to the brake linkage.
The wheel axle is connected to the brake drum. The brake lining is placed on top of the brake drum. The brake pedal is pressed. This presses the brake piston inside the brake cylinder. This compresses the air inside the brake cylinder. The compressed air is forced into the brake line. The air moves through the brake lines, pushing the brake shoes away from the brake drum.

What are air brakes used for?
An air brake slows or stops a moving vehicle. They are also commonly used on railroads and other vehicles. Air brakes are also used in emergencies, such as accidents. Air brakes are usually found on passenger cars and light freight trains.
Air brakes are also referred to as pneumatic brakes. In addition, air brakes are sometimes referred to as ‘vacuum’ brakes. There are two main types of brakes: vacuum brakes and air brakes. Vacuum brakes use the negative pressure created by the car’s movement to apply pressure to the brake shoes, and air brakes use compressed air to apply pressure to the brakes.
The purpose of air brakes is to slow or stop a vehicle. Air brakes, also called P-type brakes, are used in passenger cars and light freight trains. Air brakes are also called “air brakes” or “pneumatic brakes.”
How truck air brakes work
The most common use of truck air brakes is to slow traffic during road construction, and they are also used to slow down freight trains. There are many different types of trucks, but they all work on similar principles.
Truck air brakes consist of three basic components:
-
A compressor
-
A reservoir
-
A control valve
Compressors are devices that pressurize the air. For example, storage tanks store compressed air, and control valves regulate how much air enters the storage tank.
Air brakes are designed to be operated manually, and the driver must push a button or pull a lever to activate them. However, most drivers have controls for using their air brakes.
The brake system consists of several parts. You need brake lines, hoses, cylinders, brake pads, rods, accessories, brake drums, and brake pads.
Who invented the air brake?
The first application of air brakes was used by the New York Central Railroad in 1894 by George Westinghouse. In 1872, they were introduced to passenger service by the Pennsylvania Railroad.
The 5 components of an air brake system include:
-
compressed air tank
-
valves
-
wheels
-
brake shoes
-
brake drums
Maintenance & Safety Tips for Air Brakes
It is necessary to have air brakes on vehicles, especially trucks. They are used to stop the vehicle when it is idling or when there is insufficient momentum to keep going. Although air brakes are reliable, they require regular maintenance and safety checks.
Here you will find tips for maintaining your air brake system and keeping yourself safe while using it.
Air brake system parts
Air brake systems are complex braking mechanisms that use air pressure to press on the brake pads and slow down the moving vehicle.
At the heart of every air brake system is the caliper, which is a device that compresses and squeezes the brake pads to slow a vehicle.
The caliper is mounted on a rotating arm and has several holes for bolts that hold it in place. When air pushes on the piston, it goes against these bolts, compressing and squeezing the brake pads. The brake pads then exert pressure on the brake disks, slowing the vehicle.
A brake disk is a circular metal part that rotates with the wheel. Steel is layered on top of one another and is attached to the wheel hub. When the brake pads come into contact with the disk, friction generates heat between the pads and the disk. As a result, the disk heats up and becomes harder to turn.
A brake drum is another part of the brake mechanism. It is a circular piece of metal that holds the brake shoes. These are similar to brake pads but have different shapes. The brake shoes are pressed inside the drum and come into contact with the inner walls of the drum. Unfortunately, this also causes friction and heat generation, making the wheel harder to turn.
Why do air brakes make noise?

The noise comes from the pistons inside the brake chambers. They move back and forth, creating friction that generates heat. When the brake pads are worn, they can no longer break the car as effectively. This causes the pistons to move back and forth, generating more friction and louder noise.
Why are not air brakes used in cars?
The problem with air brakes is that they require a lot of energy to force air into the braking system, and they also wear out quickly due to the friction between the wheel and the road.
Cars do not need this type of braking system because they can rely on the car’s weight to slow them down. You only need to use air brakes when you are going over a hill or up a steep incline.
Why Air Brakes Confuse New Truck Drivers
The biggest problem with air brakes is that they do not always work properly. They can fail due to poor maintenance, wear out from excessive braking, or simply because they do not work properly. In addition, air brakes can be dangerous if not used properly. The car can roll over if the driver fails to use them correctly.
Steps to keep air brakes working in winter
The best way to make sure your air brakes work in the winter is to check and clean them regularly. If they do not work properly, look for signs of ice buildup on the braking surfaces. Also, check for leaks on the wheel bearings. If any of these problems occur, consider replacing the brake cylinders.
How do air brakes and hydraulic brakes work?
Some vehicles still use hydraulic brakes, but they are less common than air brakes. They are usually found only in heavy trucks and buses. Hydraulic brakes consist of a series of lines connected to an oil reservoir.
A valve is attached to each line so that when the driver presses the pedal, the valves open to allow oil to flow through the lines. However, as the oil flows through the pipes, it pushes against the piston, causing it to push against the drum. This causes the drum to rotate and eventually stops the vehicle.
How does the unit controller work with air brakes?

Airflow is controlled by the regulator of the compressor. It works by measuring the compressor’s air pressure and comparing it to a set point. By increasing airflow through the system when pressure falls below the set point, the regulator increases airflow through the system.
Air Brake System Parts
Air brake systems are complex braking mechanisms that use air pressure to press on the brake pads and slow down the moving vehicle.
The caliper is one of the most important elements of the air brake system; it compresses and squeezes the brake pads to slow the vehicle.
The caliper is mounted on a rotating arm and has several holes for bolts that hold it in place. The air pushes on the piston against these bolts, compressing and squeezing the brake pads. The brake pads then exert pressure on the brake disks, slowing the vehicle.
A brake disk is a circular metal part that rotates with the wheel. Several steel layers are layered on top of each other and are attached to the wheel hub. There are grooves in each layer of the disk, so heat is generated between the brake pads and the disk when they contact each other. As a result, the disk heats up and becomes harder to turn.
A brake drum is another part of the brake mechanism. It is a circular metal part that holds the brake shoes. These are similar to brake pads but have different shapes. The brake shoes are pressed inside the drum and come into contact with the inner walls of the drum. Unfortunately, this also causes friction and heat generation, making the wheel harder to turn.
Air Brake System Parts
Air brake systems are complex braking mechanisms that use air pressure to press on the brake pads and slow down the moving vehicle.
The caliper is one of the most important elements of the air brake system; it compresses and squeezes the brake pads to slow the vehicle.
The caliper is mounted on a rotating arm and has several holes for bolts that hold it in place. The air pushes on the piston against these bolts, compressing and squeezing the brake pads. The brake pads then exert pressure on the brake disks, slowing the vehicle.
A brake disk is a circular metal part that rotates with the wheel. Several steel layers are layered on top of each other and are attached to the wheel hub. There are grooves in each layer of the disk, so heat is generated between the brake pads and the disk when they contact each other. As a result, the disk heats up and becomes harder to turn.
A brake drum is another part of the brake mechanism. It is a circular metal part that holds the brake shoes. These are similar to brake pads but have different shapes. The brake shoes are pressed inside the drum and come into contact with the inner walls of the drum. Unfortunately, this also causes friction and heat generation, making the wheel harder to turn.
How do air brake systems work in modern cars?
The braking systems in cars are an important factor in the safety of these vehicles. The brake pads, which are usually made of rubber and metal, slow down the vehicle’s speed when pressed against the brake disks.
To understand how air brake systems work in modern cars, it is important to know what an air brake system is and how it works. An air brake system is a subsystem that helps brake a car more effectively by reusing the kinetic energy generated by the vehicle’s motion.
It is one of the easiest ways to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions and a very effective way to reduce pollution.
An air brake system in modern cars consists of three main parts:
-
A master cylinder
-
Brake calipers
-
Disks
The first component is the master cylinder. It is a small container filled with pressurized fluid. The master cylinder is connected to the brake pedal by a linkage. The master cylinder sends pressurized fluid to the brake calipers as soon as the driver presses the brake pedal.
The second component is the brake calipers. They contain pistons that move inward and compress the brake pads. You will notice that the calipers have many holes in them, and air can enter and exit the calipers through these holes.
Release of the brake pedal causes the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal moves the master cylinder upward, and this movement forces the fluid out of the calipers through the holes.
The third component is the brake disks. They are round metal parts attached to the wheel hubs. Grooves are cut into the outer surface of the disks, ensuring that the brake pads stay in place even after repeated use.
Air brakes are used in commercial vehicles as well as private cars. They help reduce fuel consumption and save drivers money. In addition, they do not cause damage to the vehicle and its components.
How is an air brake system constructed?
The design of an air brake system is crucial for the safety and efficiency of a vehicle.
The function of an air brake system is to allow drivers and operators to stop and hold a vehicle without wearing out the brakes.
Air brake systems use an air compressor fed by the engine to pressurize the braking system. Pistons push the brake shoes against the wheels by forcing hydraulic fluid through small hoses in the brake system.
There are two main types of air brakes: drum and disk. Drum brakes are often used in trucks and trailers because the parts wear less, and maintenance is easier for mechanics.
Disk brakes use rotors instead of drums. Rotors are made of steel plates stacked on top of each other. The rotors are located around the wheel hub and act as pistons when the brake pedal is depressed.
There are several different designs of air brakes. Some have two sets of cylinders, while others have four. The number of cylinders depends on the size of the vehicle. For example, if your car has 4 wheels, 4 cylinders are required.
Another difference between the two types of air brakes is the location of the brake cylinders. Disk brakes are located near the rear axle, while drum brakes are usually found near the front axle.
Another important feature of an air brake system is the valves, and the valves control airflow into and out of the braking system.
How to fix an air brake problem quickly and easily?
Air brake problems can be frustrating and prevent you from driving your vehicle. But do not worry; we will look at some simple steps you can take to fix this problem.
It could be due to an air brake problem. For example, if your car has been dragging or making a loud noise, it could be due to an air brake problem.
First, check the oil level in your brake fluid reservoir, it should be about 3/4 full. If there is not enough oil, the brake system may need to be flushed.
Next, check the condition of your brake pads. Are they worn out? Do they feel rough to the touch? If so, you should replace them.
Inspect the brake lines for leaks. Check all connections and fittings. Make sure everything is tight and secure.Check the condition of your brake pedals. If they are loose, tighten them.
If all else fails, contact your local mechanic, and he will be able to diagnose the problem quickly and easily. To service your air brake system for maximum safety and performance.
You should always prioritize safety when working with heavy machinery. Air brakes are essential for heavy-duty trucks and other heavy transport vehicles, and they are used if the driver needs to take his hands off the wheel for any reason.
The air brake system consists of air hoses, control valves, brake chambers, and compressed air accumulators. The hoses connecting the control valves to the brake chambers are usually rubber or reinforced rubber.
Are there any disadvantages to using air brakes?
| Aspect | Friction Brakes | Air Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Proportional to vehicle weight | Same force regardless of weight |
| Working Principle | Friction with rotating/rolling parts | Compressed air instead of rotating/rolling parts |
| Advantages | More effective for heavy vehicles | Easy to use, cost-effective, less wear and tear |
| Use Case | Common in various vehicles | An alternative for riders avoiding expensive tech |
| Emergency Braking | Dependable for emergency stops | Useful for quick stops without time for braking |
| Control over Braking Pressure | Proportional to foot pressure | Adjustable release of air pressure for control |
| Vehicle Speed Control | Allows better control over speed | Limited control over speed even with air brakes |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Where do air brakes come from?
Air brakes originated when George Westinghouse developed a new method of compressing air. He called his invention “the Westinghouse Air Brake.” It worked very well, but it did not become popular until after death.
-
How do you apply the brakes on an air brake?
The brakes are applied when the car is moving forward, and when the vehicle is stationary, the brakes are not used.
-
What is the purpose of air brakes?
The main purpose of air brakes is to safely slow down a train or car without applying the brakes manually. They are used in situations where manual braking would cause too much wear on the brakes or risk derailment.
-
What are the signs that your air brakes are working?
If you notice unusual noises coming from your car, check the brake pads first. If they look worn, you should replace them immediately. If the brakes still do not seem to be working, the problem could be elsewhere. Check the brake lines and hoses for leaks and ensure all valves are fully closed before driving.
-
What is the charging time for an air brake?
It takes about five minutes to fill an air brake tank. Remember, however, that air tanks must always be full. As the tank fills with more air, it will take longer to release the air when needed.
-
How can I tell if my air brakes are leaking?
An air leak is often hard to detect because it does not make much noise. However, you should investigate if you hear strange noises from your cars, such as a rattle or creak. You can check for leaks in several ways. One simple way is to remove the brake shoes and see if water leaks out of the holes. Another option is to stick a hose in one of the holes and see if water comes out. Finally, if the brake disk does not drain, you can spray water on it and see if it drains.
-
How do I benefit from this technology?
You know how important brakes are if you have ever driven a vehicle. Without them, driving would be a very dangerous experience!
The technology used in air brakes helps make driving safer for everyone. It is an ABS braking system that uses compressed air to create pressure to slow or stop your vehicle. This makes stopping in emergencies easier and reduces the force needed to slow or stop your vehicle.
-
When should you use an air emergency brake?
Cars need emergency brakes designed for emergencies, and these brakes should never be used to replace the normal braking system.
Emergency brakes are used in extreme cases, such as when a driver cannot apply the brake pedal normally.
-
Do all trucks have air brakes?
Air brakes are the primary braking system for trucks, but other methods can slow down these huge vehicles.
Compressed air is used to create pressure and release or apply the brakes on vehicles. They come as single or multiple systems, usually accompanied by a warning device such as a bell, horn, or light. In the “two-pipe” configuration of the air brake, two pressure lines connect the motor to both brakes.
It is most commonly found on trucks and buses because it provides strong stopping power and is relatively easy to maintain.
Conclusion
Knowing how air brakes work is important to understand why you need one, how to find the right air brake for your needs, and what to expect from it. Air brakes use compressed air to slow and stop cars. They are most commonly found in passenger cars and are used with a differential. However, there are other uses for air brakes, including trains and airships. Air brakes are excellent for reducing the likelihood of a traffic accident. However, one disadvantage of air brakes is the cost of maintenance and replacement parts. Consider switching to an air brake system if you find that your car’s brakes are not working well enough.
