Braking Unveiled: The Symphony of How Car Brakes Work
Zooming down the open road or navigating busy city streets, your vehicle’s ability to come to a swift, controlled halt is a testament to the intricate dance of its brake system. Much like a well-choreographed performance, car brakes are the unsung heroes that transform velocity into serenity with a single command – your foot on the pedal.
Let’s unveil the captivating mechanics behind this modern marvel and unravel the science that empowers you to stop on a dime, all while ensuring safety and control. Welcome to the fascinating world of how car brakes work, where physics and engineering unite to provide a symphony of security.
Braking System Basics
| Braking System Basics | Description |
|---|---|
| Components | Brake pedal, brake master cylinder, brake lines, brake calipers, brake pads, brake rotors |
| Purpose | Slow down or stop the vehicle’s motion |
| Principle | Regular inspection, brake fluid checks, pad, and rotor replacement |
| Types of Brakes | Disc brakes and drum brakes |
| Brake Fluid | Transmits hydraulic force from the brake pedal to the brake components |
| Friction | Generated by brake pads or shoes pressing against brake rotors or drums |
| Hydraulic Pressure | Amplifies force applied to the brake components |
| Kinetic Energy Conversion | Converts the vehicle’s motion energy into heat energy |
| Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) | Prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection, brake fluid checks, pad and rotor replacement |
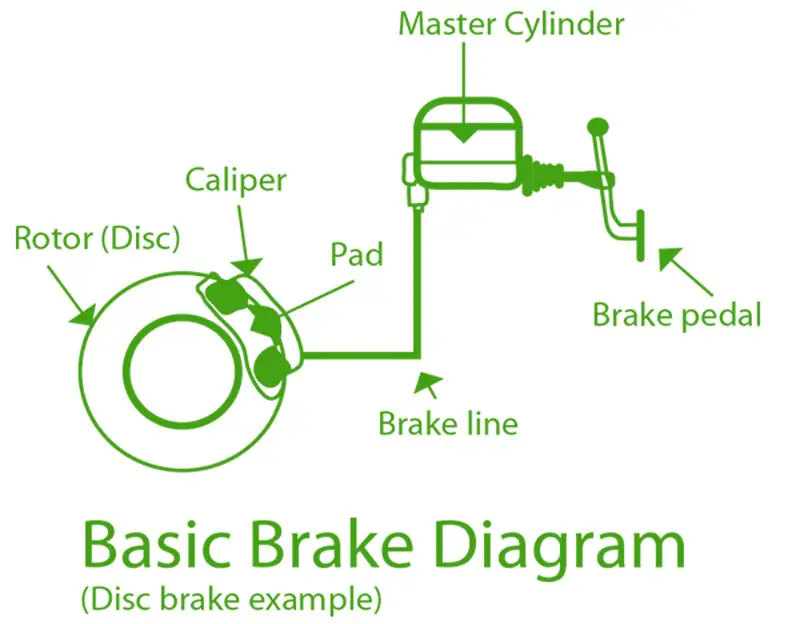
How do Car Brakes work?
Car brakes are a crucial component of your vehicle’s safety system, enabling you to slow down and come to a stop whenever needed. The basic principle behind car brakes involve converting kinetic energy (the energy of motion) into heat energy, dissipating it to halt the vehicle. This process relies on friction and hydraulic pressure to ensure effective braking. Let’s delve into the details of how this intricate system functions:
- Friction and Brake Pads: Pressing the brake pedal activates a hydraulic system that sends brake fluid to the brake calipers at each wheel. These calipers squeeze the brake pads onto the spinning brake rotor (a brake disc) attached to the wheel. The friction between the brake pads and the rotor slows down the wheel’s rotation.
- Hydraulic Pressure: The pressure created when you press the brake pedal amplifies the force applied to the brake pads. This multiplication of force is crucial for effectively stopping a moving vehicle, especially larger and heavier ones.
- Kinetic Energy Conversion: As your car is in motion, it possesses kinetic energy. The friction generated by the brake pads rubbing against the rotor converts this kinetic energy into heat energy. This heat is then dissipated into the surrounding air. The more efficient the braking system, the more kinetic energy is transformed into heat, enabling the vehicle to decelerate or come to a stop.
- Disc Brakes and Drum Brakes: Modern vehicles primarily use disc brakes or drum brakes. Disc brakes operate by clamping brake pads onto a spinning rotor, as described above. On the other hand, drum brakes feature brake shoes that press against the inside of a drum-shaped component attached to the wheel. While both systems accomplish the same goal, disc brakes are generally more effective at dissipating heat, making them common in vehicles today.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): To prevent the wheels from locking up and skidding during hard braking, modern cars are equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). ABS rapidly modulates the brake pressure on each wheel, allowing the driver to maintain steering control while stopping the vehicle.
- Brake Fluid and Maintenance: Brake fluid plays a vital role in transmitting the force from the brake pedal to the brake components. Regular maintenance and ensuring an adequate level of clean brake fluid are essential for properly functioning the brake system.
In essence, car brakes work by harnessing the power of friction and hydraulic pressure to transform your vehicle’s energy of motion into heat, allowing you to control your speed and bring your car to a stop safely. Understanding the mechanics behind this process underscores the importance of maintaining your vehicle’s brakes for both your safety and the safety of others on the road.
HOW DO CAR BRAKES WORK WHEN THEY FAIL?
If the brakes don’t work properly, the wheel may not slow down enough for the engine to pull it away from the ground. In this case, the wheel continues to spin until it reaches a certain point. At this point, the tire bursts, and the rim breaks off. This is known as a “lock-up” event.
It’s every driver’s worst nightmare: you’re cruising down the highway, and suddenly your brakes fail. Fortunately, there are a few things you can do to stay safe in this situation. First, try to stay calm and avoid panicking.
Second, gently ease your foot off the gas pedal and onto the brake pedal. If your car has an automatic transmission, shift into low gear. This will help to slow the car down without overworking the engine.
Finally, use your emergency brake to stop the car gradually. Although it’s not ideal, it’s better than slamming on the brakes and risk losing control of the vehicle. With a cool head and a little bit of know-how, you can safely navigate your way through this stressful situation.
You Also Like: Can You Put Brembo Brakes On Any Car?
Signs the Braking System Isn’t Working Properly
A properly functioning braking system is paramount for the safety of you, your passengers, and others on the road. Detecting signs of a malfunctioning braking system early on can prevent accidents and ensure timely repairs. Here are several key indicators that your braking system may not be working properly:
- Spongy Brake Pedal: If the brake pedal feels soft, spongy, or goes too far down when you apply pressure, it might indicate air in the brake lines or a potential brake fluid leak. This can compromise the braking force and responsiveness.
- Brake Warning Light: The brake system warning light on your dashboard illuminates when there’s an issue with the braking system. It could indicate low brake fluid, a malfunctioning ABS, or other brake-related problems.
- Screeching or Grinding Noises: Unusual noises when braking, such as screeching or grinding sounds, often suggest worn brake pads. Metal-on-metal grinding indicates that brake pads are severely worn, which can damage the rotors and reduce braking efficiency.
- Vibration or Pulsation: Vibrations or pulsations in the brake pedal or steering wheel during braking could be due to warped brake rotors. This can result in uneven braking performance and an uncomfortable driving experience.
- Pulling to One Side: If your vehicle pulls to one side while braking, it might indicate uneven brake pad wear, brake fluid imbalance, or a sticking brake caliper. This can compromise steering control and create a safety hazard.
- Increased Stopping Distance: If your vehicle takes longer to stop than usual, it’s a clear sign that the braking system isn’t functioning at its best. This can be caused by worn brake pads, contaminated brake fluid, or other issues.
- Burning Smell: A strong burning odor while driving or after stopping could indicate overheated brakes. This might be due to dragging brake components or severe brake system issues. Overheated brakes can compromise braking effectiveness.
- Fluid Leaks: Puddles of clear or brownish fluid beneath your vehicle might be a sign of a brake fluid leak. Brake fluid leaks can lead to decreased braking performance and potential loss of braking ability.
- Dashboard Warnings: Modern vehicles often have electronic systems that monitor the braking system. If any error codes related to the braking system appear on your vehicle’s display, it’s a clear indicator that professional attention is needed.
- Hard Brake Pedal: If your brake pedal feels unusually hard and requires excessive force to depress, it could signify a vacuum-related brake booster issue or a failing master cylinder.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to address them promptly. Ignoring braking system problems can lead to compromised safety, increased repair costs, and potential accidents. If you’re unsure about the condition of your braking system, it’s always recommended to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic.
How do car brakes work together?
Car brakes work together to stop your car. The engine activates brakes in order to create the friction needed to halt your vehicle. The sequence of parts that make up a brake system is connected in a way that allows for safe and precise stopping power.
The brake system consists of three main components: the master cylinder, the brake lines, and the brake discs/drums.
- Master Cylinder
The master cylinder is located under the hood and contains hydraulic fluid. It connects to the brake line and controls how much force is applied to each brake.
- Brake Lines
Brake lines connect the master cylinder to the individual brake drums/discs. Each brake line has a reservoir inside the master cylinder where the brake fluid is stored until needed.
- Brakes Discs/Drums
Brakes discs/drums are attached to the wheel hubs. There are usually four discs/drums per wheel. These discs/drums contain friction material that creates friction when the brakes are applied.
How do car brakes work with other systems?
Car brakes work with other systems, such as the steering, suspension, and engine. When you press down on the brake pedal, a hydraulic system sends brake fluid to the calipers and engages your brake pads. The calipers ensure that the brake fluid is delivered to the pads, which in turn apply pressure to the rotors.
When you release the brake pedal, the hydraulic system releases the pressure from the calipers, and the pads return to their original position.
Do cars brake with all 4 wheels?
Yes, most modern cars brake with all four wheels. The braking system in a typical passenger vehicle is designed to distribute braking force among all four wheels to ensure optimal stopping performance and stability. This approach maximizes the friction between the tires and the road surface, allowing for more efficient and controlled deceleration.
In vehicles with a four-wheel disc brake setup, each wheel has its own brake rotor and brake caliper, and all four wheels contribute to the braking process. When you press the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is transmitted to each brake caliper, which then squeezes the brake pads against the brake rotors. This friction between the pads and rotors slows down the rotation of all four wheels simultaneously.
Furthermore, vehicles equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) are capable of individually modulating brake pressure on each wheel to prevent skidding and maintain steering control. This feature enhances the ability to brake effectively and maintain stability, especially in emergency situations or on slippery surfaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is my brake pedal feeling soft and spongy?
A soft and spongy brake pedal often indicates air in the brake lines, causing reduced hydraulic pressure. This can compromise braking efficiency and requires bleeding the brake system to remove air bubbles.
2. My brakes are making a grinding noise. What could be the issue?
Grinding noises while braking usually point to severely worn brake pads that have exposed the metal backing. This can damage the rotors and diminish braking performance. Promptly replace the brake pads to prevent further damage.
3. My vehicle pulls to one side when braking. What’s causing this?
Uneven braking performance leading to pulling to one side can be due to factors like uneven brake pad wear, a sticking brake caliper, or brake fluid imbalance. Have your braking system inspected to identify and address the underlying issue.
4. How often should I replace my brake pads and rotors?
The replacement interval varies depending on driving habits, vehicle type, and the quality of components. Generally, brake pads last around 30,000 to 70,000 miles, while rotors can last longer. Refer to your vehicle’s manual and consult a mechanic for personalized guidance.
5. Can I drive with the ABS warning light illuminated?
The ABS warning light indicates a problem with your Anti-lock Braking System. While you can still drive without ABS functionality, it’s advisable to have it inspected promptly, as the system won’t function as intended during emergency braking situations.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy braking system is vital for safe and confident driving. Familiarizing yourself with common brake-related issues and their solutions empowers you to take action when needed. Regular inspections, timely repairs, and heeding warning signs contribute to keeping your braking system in top shape, ensuring your safety and the safety of those around you on the road. If you’re ever uncertain about the condition of your brakes, seek professional advice from a qualified mechanic to maintain optimal braking performance.
