Workings Of A Brake System – Components, And Auto Circuit
Brake systems have three major components: the master cylinder, wheel cylinders, and brake lines. The master cylinder has two chambers separated by a plunger.
When the driver applies pressure to the pedal, the pressure forces the plunger into the chamber. This generates hydraulic fluid under high pressure, which flows from the master cylinder to the wheel.
The wheel cylinders push against the pads or shoes attached to the wheels. Friction between the pad and the disk causes heat.
This heat dissipation over time eventually wears the pads out. If the pads become too worn, the vehicle won’t stop correctly.
What are the components of a brake, and how do they work?
The brake system comprises several components that work together to slow down your car and safely bring it to a stop. These include:
Master Cylinder
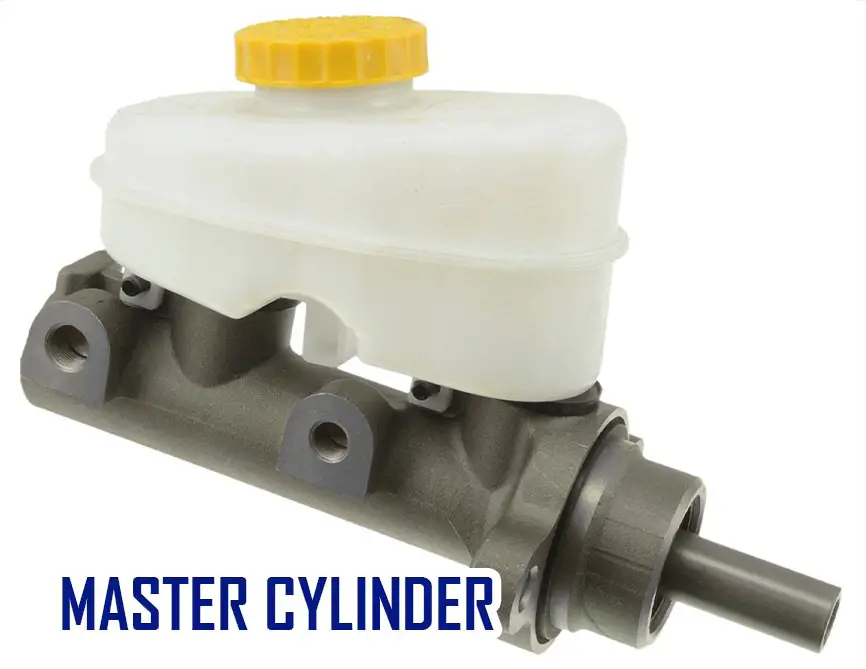

A master cylinder is a component that connects your brakes to your braking system. It contains two chambers: one for fluid and one for air.
The two chambers are connected by a piston which moves up or down in response to pressure from the pedal. When you press the brake pedal, it pushes the piston down into the chamber with the fluid.
This causes the piston to push against the chamber’s walls, creating a vacuum inside the room.
As the vacuum increases, the pressure builds up inside the chamber until it reaches a certain point where it forces the piston back out of the chamber. This releases the pressure in the room and allows the brakes to apply force to the wheels.
The first type of master cylinder was invented in 1892 by German engineer Wilhelm Maybach. He called his invention an “Automatic Motor Vehicle Master Cylinder” because he believed this new device would make driving safer.
Maybach’s design became so popular that it eventually led to the development of modern-day hydraulic systems.
Wheel Cylinders
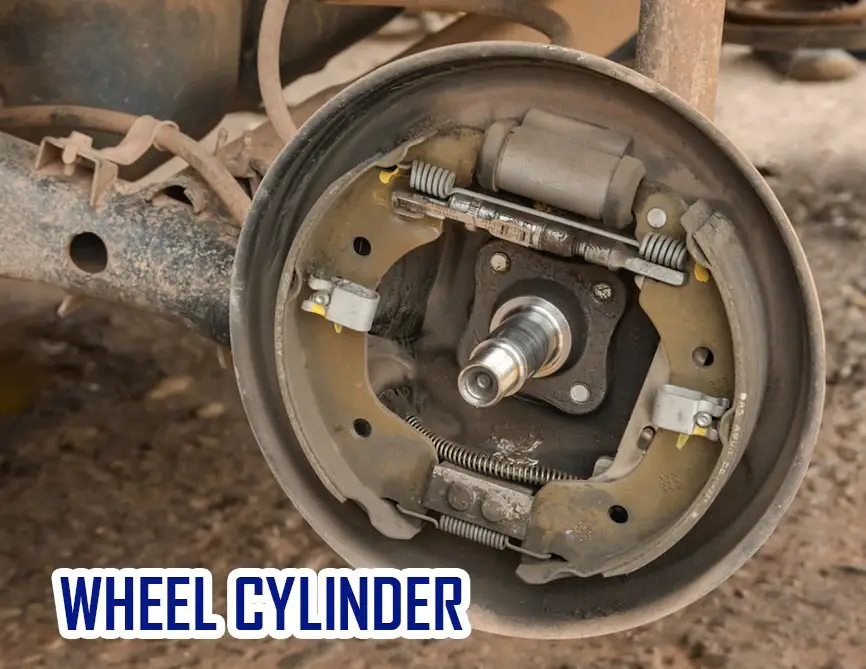

Wheel cylinders are used on vehicles with disc brakes. They contain two chambers: one for oil and one for air. A piston moves back and forth within each chamber.
When you press the brakes, the piston moves downward, forcing oil through a pipe to the caliper. The calipers squeeze the pads against the rotor, applying friction to slow the vehicle.
Brake Lines
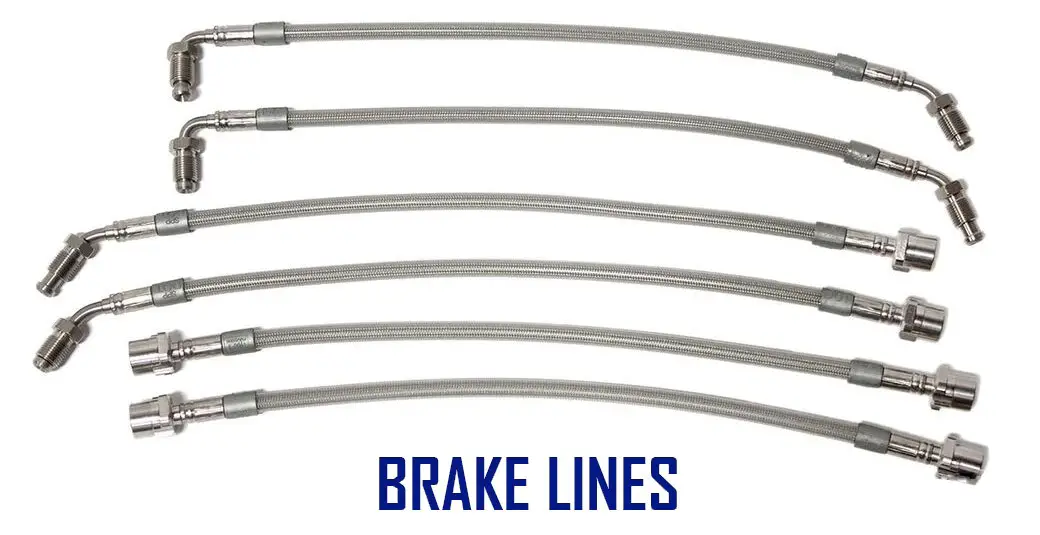

A brake line connects the master cylinder to each brake caliper. A brake line consists of a flexible hose, a rigid tube, and fittings at both ends.
The flexible hose allows air to flow through it while the rigid tube keeps the brake fluid from leaking out. At the end of the rigid tube, a fitting called a union attaches to the brake caliper. This union is where the brake line meets the brake caliper.
Pads
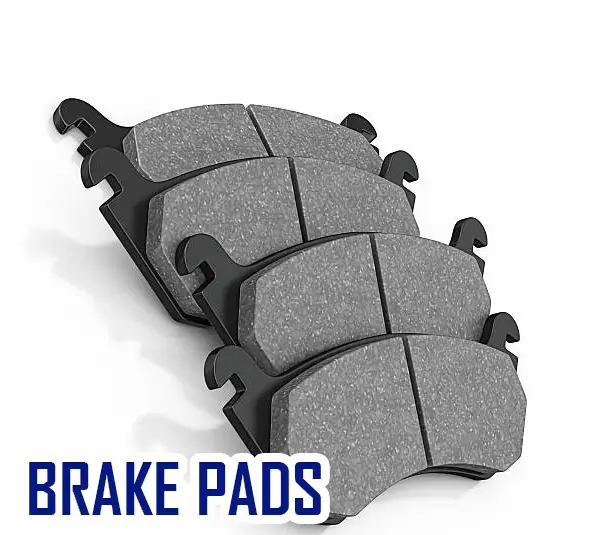

Brake pads are made of rubber or similar material. When they come in contact with the rotor, they expand slightly.
Then when the brake pedal is pressed, the pistons move up and down, pushing the pads further apart. The pads then rub against the rotor, slowing the car.
Rotors
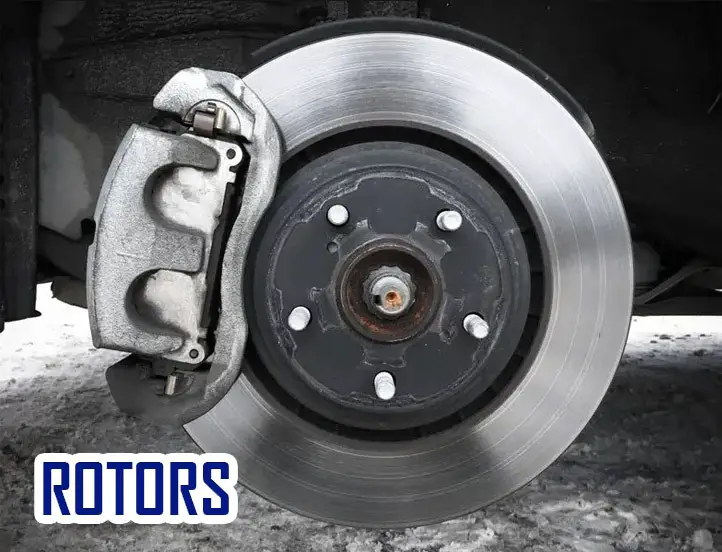

The most important component in the braking system is the rotor or disc attached to the wheel and acts as friction material for stopping the car.
It has two sides: one side that faces the road and another side that faces the hub. There are a pair of brake pads on different sides of a rotor.
When the brake pedal is pressed, the brake pads rub against the rotors creating friction that causes the vehicle to stop or slow down.
Calipers
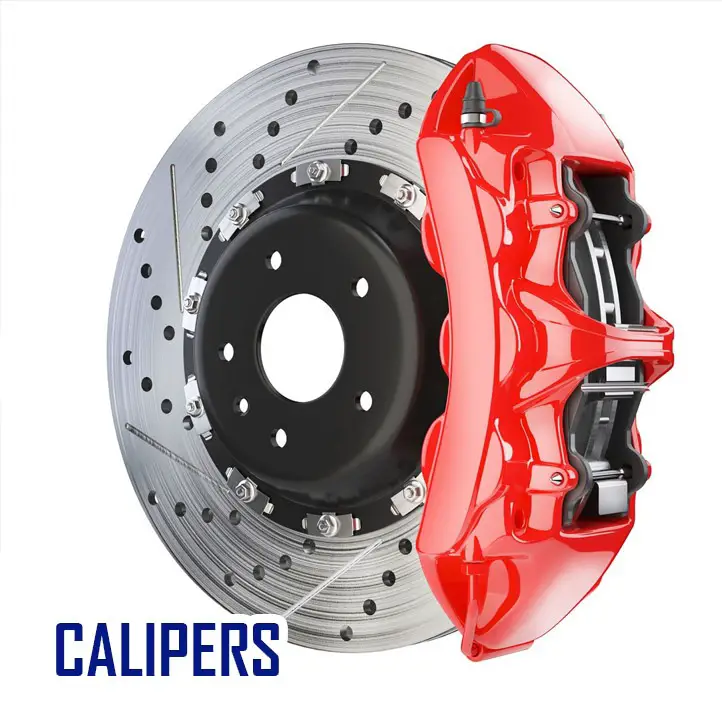

A brake caliper holds the brake pads and piston. When the brake pedal is pressed, the force travels to the calipers via a complex system and the caliper presses the pads to rub against the rotors to provide the necessary friction to slow down the vehicle.
Anti-Lock Brake System
Anti-lock braking systems prevent skidding by applying pressure to the brakes during emergencies. These systems also reduce stopping distances.
Electronic Stability Control

Electronic stability control uses sensors to monitor the speed and direction of the car. If the car begins to veer too far left or right, the electronic stability control system automatically applies pressure to the brakes to bring the car back under control.
Brake Circuit Design
The brake circuit design is a closed circuit. This means that any hydraulic pressure in the system remains within the system.
The master cylinder pressurizes brake fluid when you use the brake, which then travels through hoses and pipes until it’s applied to one of the car’s wheels by a caliper piston.
The size of this piston determines how much force is needed to stop the wheel from rotating (i.e., how hard you have to press down on your brakes).
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQs]
1. What Is A Brake System?
A brake system is part of an automobile’s braking mechanism. It is designed to stop the vehicle quickly and smoothly.
2. How Does A Brake System Work?
When you apply the brakes, the brake shoes squeeze onto the drum or disk. As they do so, the brake fluid is forced into the wheel cylinders.
The wheel cylinders push the pistons outward, causing them to compress the brake lines. The compressed brake lines transfer the force to the calipers, which clamp the brake pads tightly onto the rotor.
The friction between the pads and the rotors slows the rotation of the wheels, thus slowing the vehicle. if you need more information about how a brake system work
read the article.
3. Why Do We Need Brakes?
We use brakes because they allow us to stop our cars without having to run into people or objects. When you drive, you want to be able to stop as soon as possible.
4. What Are The Components Of A Brake System?
Brakes are made up of many parts: the brake pedal, the master cylinder, the brake lines, the calipers, the brake pads, the rotors, the wheel cylinders, etc. All these parts work together to make sure that your car stops properly.
5. What Is The Difference Between Disc Brakes And Drum Brakes?
Disc brakes are more common than drum brakes. Disc brakes are found on most new cars today. Drum brakes were once very popular, but now they’re rarely seen.
6. What Is A Drum Brake?
A drum brake is a type of braking system where the brake shoes are attached to a metal ring inside a drum. The brake shoe is pushed against the outside of the drum, creating friction with the drum. The friction causes the drum to slow down.
7. What Is A Clutch?
The clutch is a device that connects the engine to the transmission. A clutch allows the driver to shift gears manually.
Conclusion
Your car’s brake system comprises hydraulic, mechanical, and pneumatic components. These are all designed to work together to ensure that when you press the pedal, your brakes respond correctly.
